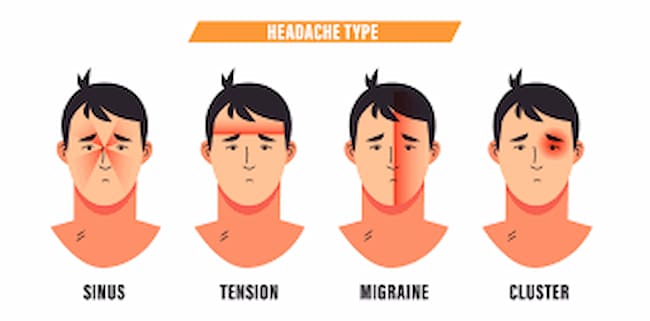
Pressure Headache Symptoms
headache pain in the eyes, headache pain while talking or swallowing, headache while bending over.
Ear ringing treatment natural:
wax can block your ear canals and cause muffled hearing plus an annoying buzzing sensation. natural medicine menopause treatment.- change any behavior that is dangerous or harmful to your health; lose weight; get exercise; eliminate stress in your life; drink plenty of water, take deep breaths and go for a walk-in park relax meditate imagine a vision of yourself like you like yourself listen to music yoga sunbath.-
Ear wax removal home remedy:
earwax or cerumen is a natural substance made by the ears to clean and lubricate the ear canal. if you have an itchy feeling in your ears, try these home remedies for instant relief. this homemade solution works great to soften ear wax naturally and make it easy to remove from the canal with a cotton swab or softening drops.
The best medicine for tension headache:
1. Ice pack;
2. Ice on the neck;
3. Ice on the shoulders and upper back;
4. Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid);
5. Acetaminophen (Tylenol).
6. Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin).
7. Naproxen Sodium (Aleve)
Tension headache back of the head:
1. Exercises for the neck
2. Relaxation techniques
3. Deep breathing exercises
4. Meditation
5. Biofeedback training
6. Yoga or Tai chi
7. Massage therapy
Types of headaches:
1. Cluster headache
2. Trigeminal neuralgia
3. Tension-type headache
4. New daily persistent headache
5. Migraine headache
6. Psychological factors causing headaches
7. Headache with visual disturbance/ aura
8 Post tension syndrome
9 Unknown cause of headaches
10 Other types of chronic daily headaches
11 Acute onsets of severe headache
12 Severe but short-lived pain occurring mostly in children
13 Other causes of acute, severe headache
14 Sinus or facial congestion
15 Neurological diseases that may be the cause
16 Cerebrovascular disease
17 Headaches treated with prescription medications
18 Uncommon causes
19 Warning signs
20 About Acute Headache
a tension headache causes:
1. Prolonged stress
2. Muscle tension in the neck, shoulders, or upper back;
3. Physical injury to the head or neck;
4. Neck sprain due to whiplash
5. Eyestrain
Barometric pressure headache symptoms:
tension headache, neck pain shoulder pain migraine-like head- neck pain neck stiffness neck or shoulder muscle spasm aching in the upper part of the chest.
Ear ringing causes:
ear ringing is a symptom, not a diagnosis. it can occur with many different underlying conditions and requires proper evaluation by an otolaryngologist. some causes include ear infection, injury, side effects from certain medications, hyperacusis (a sensitivity to noise), age-related hearing loss, as well as various disorders affecting the inner ear including Ménière’s disease and vestibular neuritis.
10 ways to avoid headaches at work:
1. Find the right workstation
2. Learn some simple exercises to keep your muscles relaxed at your desk
3. Practice stress management skills, such as deep breathing or yoga
4. Be sure you’re getting enough sleep, rest, and exercise during the week
5. Minimize exposure to triggers that may cause headaches for you, like fluorescent lights or smoke from secondhand tobacco smoke
7. Get treatment for any conditions that are contributing to headaches, including chronic sinus infections or high blood pressure
8. Take preventive medications if recommended by your doctor for migraines or daily headaches
9. See an occupational health professional who can help identify ways to reduce stressful situations on the job
10 Make sure you have a good understanding of your options for headache treatment.
Low blood pressure headache symptoms:
> Headache
> Blurred vision
> Nausea or vomiting
> Confusion/ trouble thinking clearly
> Dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting spells, being more easily tired than usual.
Rebound high-pressure headache symptoms:
1. Headache
2. Nausea or vomiting
3. Dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting spells, being more easily tired than usual.
4. Blurred vision/ seeing spots/floaters
5. Ringing in the ears known as tinnitus
6. Difficulty concentrating or difficulty sleeping due to headache
7. A feeling of “pressure” behind one eye that seems to come and go over several days or weeks
8 If you think you may have rebound headaches talk with your healthcare provider about treatment options before you cause further damage to your head by neglecting it; avoid taking pain medications every day for headache relief even if they make you feel better initially because long-term use can actually make headaches worse.
5 wonder foods for headache:
1. Basil, ginger, and green chili- have an anti-inflammatory effect on the body. Basil is a natural decongestant, while green chilies are known to ease stomachache and ginger helps in the relaxation of muscles.
2. Cabbage juice:
Rich in vitamin B6 that helps in relieving muscle pain and migraines that are commonly associated with tension headaches. ..
3 Ice cream:
Milk contains tryptophan which helps the brain produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates moods and sleep cycle. Caffeine in chocolate is a vasodilator; it expands blood vessels, including those in the head…
4. Tomatoes :
Vitamin B1 and folate in tomatoes work as a natural anti-depressants. Vitamin C helps treat blood vessel spasms and headache-associated high blood pressure…
5. Grapes:
Grapes contain resveratrol, a powerful antioxidant that lowers stress hormones by relieving inflammation caused by stress. Resveratrol also lowers the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Barometric pressure headache symptoms:
Headache Pain
Nausea or vomiting
Dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting spells, being more easily tired than usual.
Blurred vision/ seeing spots/floaters
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) has 1 of 2 characteristics:-
pulsatile or non-pulsatile continuous tone(s) moving from ear to ear. The intensity is proportional to pulse pressure changes observed by the examiner. When systolic BP falls beyond a certain cutoff level the tinnitus will be heard.
The pulsation is normally 120 bpm +/-30 bpm with ∼a 50% duty cycle, but it can be faster if measured during the systolic upstroke phase of the BP waveform. If there is no pulsation the tinnitus may be continuous in intensity. The examiner should observe for 1 min to ensure that there are no changes in frequency, timbre, or volume during BP variations.