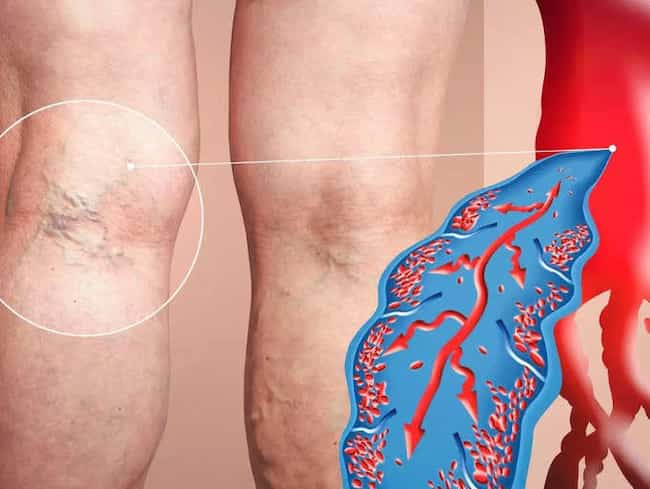
Leg Clot Causes
The formation of a blood clot in the leg is a common problem. It can cause pain and swelling. The most common cause of a blood clot in the leg is a lack of movement. This can happen if you are bedridden or stay in one position for a long time. Some other causes of blood clots include:
• Damage to the blood vessels lining the inside of the leg from injury or surgery
• Inherited disorders that make your blood more likely to form clots
• Cancer or its treatment
• Being overweight or obese
• Smoking cigarettes
• Taking estrogen-containing medications, such as birth control pills or hormone therapy drugs
• Pregnancy
• Problems with the valves in the veins of your legs
• Inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Possible symptoms of blood clots in the leg:- Some people have no symptoms from a blood clot in their portion. When there are symptoms, they can include:
• Swelling and pain that gets worse over time if the blood clot blocks circulation to your foot or toes (known as deep vein thrombosis)
• Warmth over the affected area because it is not getting enough oxygen-rich blood (known as cellulitis)
Treatment for a blood clot in the leg:
If you are diagnosed with a blood clot in the leg, your doctor may prescribe anticoagulant medication to help dissolve the clot. If you have difficulty walking or the chunk is large, your doctor may also recommend surgery to remove the clot.
In some cases, compression stockings may be prescribed to help improve blood flow in the leg. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help you regain strength and mobility in your leg.
Blood clots can also form in other body parts, such as the lungs. Therefore, if you are experiencing shortness of breath, chest pain, or rapid heart rate, it is essential to seek medical attention right away, as these may be signs of a pulmonary embolism (PE).
PEs occur when blood clots form in the veins of the lower body and travel to the lungs. PE can lead to shortness of breath, chest pain, or even death if left untreated.
How to prevent blood clots:
The risk of blood clots can be minimized by staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, drinking plenty of fluids, and getting enough sleep. For example, suppose you are traveling for long periods or bedridden due to an illness or injury. In that case, it is essential to frequently exercise your legs and wear compression stockings to reduce the risk of developing blood clots.
Blood clot in the leg:
Suppose you experience pain in one leg that does not improve with rest, swelling in your leg or foot. In that case, you seek medical attention immediately when the redness in your skin is near the affected area or discoloration (such as black-and-blue marks). These may be signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when blood.
Clot forms in one of the deep veins in your legs. It is essential to receive treatment for DVT right away, as it can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
Sudden stabbing pain in the calf, thigh, or groin – this type of pain is often worse when you stand up from sitting or lying down for an extended period. This kind of pain typically comes on suddenly and can be very intense. You might also feel a burning sensation.
The pain may last only a few minutes before going away, although it can come back later. It can happen several times a day. It’s usually easiest to relieve the pain by elevating the leg and flexing (bending) the foot up and down.
Warmth, redness, swelling, and tenderness in one part of the leg. It usually happens along with pain or a heavy feeling. The skin might be warm to the touch. Swelling may occur around the ankle or below the knee.
If you touch it, you’ll probably feel something hard under your skin. This condition has many different names; we call it erythema nodosum. Sometimes it’s called periarteritis nodosa.
Early-stage blood clot in leg symptoms:
Sudden stabbing pain in the calf, thigh, or groin – this type of pain is often worse when you stand up from sitting or lying down for an extended period. This kind of pain typically comes on suddenly and can be very intense. You might also feel a burning sensation.
The pain may last only a few minutes before going away, although it can come back later. It can happen several times a day. It’s usually easiest to relieve the pain by elevating the leg and flexing (bending) the foot up and down.
Warmth, redness, swelling, and tenderness in one part of the leg. It usually happens along with pain or a heavy feeling. The skin might be warm to the touch. Swelling may occur around the ankle or below the knee. If you touch it, you’ll probably feel something hard under your skin. This condition has many different names; we call it erythema nodosum. Sometimes it’s called periarteritis nodosa.
Chronic blood clot in leg symptoms:
Chronic thrombosis (blood clots) of the veins results in pain and swelling of affected areas, usually legs and feet. A chronic blood clot can last for months to years before completely disappearing on its own after the damage has occurred to surrounding tissue or organs.
Symptoms vary widely depending on whether an acute episode (short-term lasting less than six weeks) develops first, which can be accompanied by superficial phlebitis (inflammation of a vein just under the skin), or in cases of untreated, deep vein thrombosis, can lead to the development of the post-thrombotic syndrome.
Skin that turns pale or blue:
Skin that turns pale or blue can signify an underlying problem with oxygen flow in the blood. In general, this condition is caused by some blockage in arteries or veins that carry blood to and from the surface of your skin – usually because of clogged arteries (atherosclerosis) or clogged veins (phlebitis).
Skin sores that won’t heal:
Depending on their cause, sores may develop anywhere in your body. Some common types are:-
1) Abrasions: Also called scrapes, they happen when you directly contact something sharp like gravel or glass. You might not notice this kind of wound immediately since it can take time to bleed and the irritated skin to separate.
2) Ulcers: A break in the skin that won’t heal on its own or gets worse over time, often forming a bumpy red border on your skin. Also, any sore on your body that doesn’t go away within three weeks should be checked by a doctor.
Abrasions:
These are common injuries of the knees, elbows, and hands due to minor scrapes with sharp edges or objects like glass, metal, or wood. It is observed as an area of injury where both the dermis (thick) and epidermis (thin) are torn down, exposing subcutaneous tissues under them, causing bleeding through capillaries into surrounding lymphatics, then it becomes swollen and erythematous.
Ulcers:
An ulcer is a lesion that does not heal within three weeks. The most common cause of nonhealing ulcers is an infection, which can delay or prevent healing. Other causes of nonhealing ulcers include vascular disease (such as peripheral arterial disease or diabetic foot), radiation therapy, and some types of cancer. If you have an ulcer, it’s essential to see your doctor to find out the underlying cause to be treated.
Symptoms of a blood clot can include:
1. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) symptoms:
Pain in the affected area, which may worsen over time
Swelling of the leg
Warmth and redness in the leg
Tenderness to the touch
2. Pulmonary embolism (PE) symptoms:
Chest pain – this may be severe and feel like it’s crushing your chest b. Shortness of breath c. Coughing up blood d. Rapid heart rate, e. Anxiety
3. Claudication:
Painful cramps in the calf muscles after walking a short distance b. The cramps go away with rest c. There is usually no swelling or redness d. This condition is caused by a lack of oxygen in the muscles due to narrowed or blocked arteries
Chronic blood clot in leg treatments:
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for chronic blood clots in the leg. Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the lump. However, some general steps that can be taken to treat a blood clot include:-
1) Taking medication to thin the blood and help it move more freely through your veins, such as heparin or warfarin
2) Elevating your legs above heart level when possible to help reduce swelling
3) Wearing compression stockings to help improve blood flow
4) Exercising regularly to improve circulation
5) Quitting smoking, which can damage your veins and make it more difficult for blood to circulate
6) Avoiding long periods of sitting or standing to help prevent blood from pooling in your veins
7) Taking steps to manage any underlying health conditions that may have contributed to the clot, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart disease
8) Considering surgery to remove the clot if it’s causing significant problems or doesn’t respond to other treatments
Blood clot in the arm:
A blood clot in your arm (also called a deep vein thrombosis or DVT) can be severe and requires medical attention. A DVT is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein, usually in the arm or leg. If the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, it can cause a fatal pulmonary embolism (PE).
Symptoms of a blood clot in the arm can include:
1) Pain in the arm, which may get worse over time
2) Swelling of the arm
3) Warmth and redness in the arm
4) Tenderness to the touch
5) Difficulty moving or using the arm
6) Chest pain if there is also a blood clot in the lung