What is Stage 4 Cancer?
Stage 4 cancer refers to the most advanced form of cancer. It has spread from its original site, or nearby tissue, into nearby or distant parts of the body.
What are chemotherapy and radiation?
Chemotherapy is a therapy process that uses certain drugs to kill tumor cells. Chemotherapy may also be used, along with other treatments, to keep cancers under control during remission (i.e., when tumors have not returned). Radiation therapy uses high-energy x rays to kill cancer cells.
This type of radiation is delivered by a machine aimed at the area where the cancer is found. It usually causes minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue because it is narrowly focused on just part of the body. Some patients prefer these treatments as an alternative to surgery.
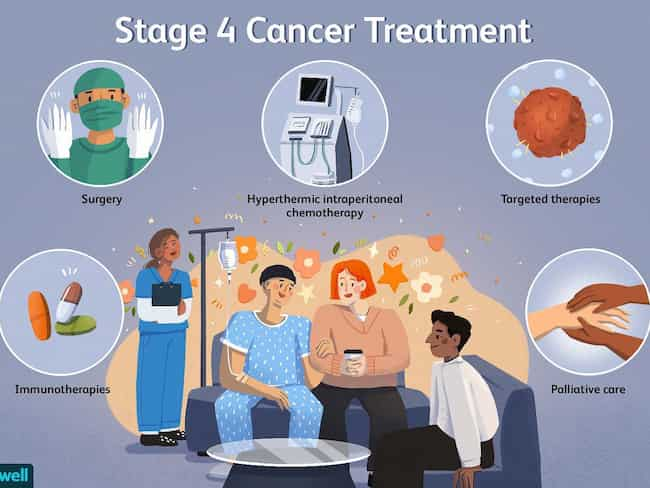
How is stage 4 cancer treated?
Patients with stage 4 cancer may have a variety of treatments at the same time or in place of each other. It depends on many factors, including the patient’s age and overall health, type of cancer, possible side effects from treatment, and personal preferences. In every case, the goal of treatment is to prolong life as long as possible while maintaining the quality of life as much as possible.
Treatment for advanced cancer must be monitored closely by experienced physicians because it can cause serious complications even when it produces an initial remission that can last several months or years. This period is sometimes called a “silver lining” because its effect can sometimes make a patient feel better for a short time before his or her condition worsens again.
Chemotherapy is the treatment for cancer that uses certain drugs to kill tumor cells. It may also be used, along with other treatments, to keep cancers under control during remission (i.e., when tumors have not returned).
Chemotherapy can prevent the growth of new blood vessels needed by tumors to grow. Further, chemotherapy can delay or stop the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body, especially in the early stages of cancer.
For many patients who have stage 4 cancer, chemotherapy is given as a combination therapy with surgery and/or radiation therapy if available. In most cases, a patient’s response to chemotherapy is assessed after a few weeks of treatment has occurred so that special adjustments can be made to obtain the best result.
The most common side effects of chemotherapy are fatigue, sore throat, nausea and vomiting, hair loss, mouth sores, or rashes on the skin. But treatment can be modified so that toxicity is minimized while maximizing benefit.
How long from stage 1 to stage 4 cancer:
From diagnosis, at Stages 1,2,3, and 4, the average survival times are as follows. Stage One (1) can be about three years, Stage Two (2) is five years; Stage Three (3) survival time is now about one year, and if still no treatment it could be six months; finally with Stage Four (4) it may only be a few weeks. If you include all types of cancer comprising roughly 100 different diseases, then this makes up the deadliest killers known to mankind. Even though there are over 100 different cancers perhaps the four most common would be; Breast (female), Lung (male and female), Colon (bowel), and Prostate (male). The Bot has chosen the most common of these four.
why is stage 4 cancer incurable:
Again the bot has chosen the most common of these four. The main reason is that when cancer spreads to distant places in our body, it becomes too late for us to do anything about it. We have already said enough in our detailed explanation above, so no more repeating.
stage 4 cancer survival rates:
The chances of surviving Stage Four Cancer are very slim. If diagnosed at stage 4, your doctor would give you between 6-12 months to live without treatment; with treatment, it could be 6 years or more; whereas if you are lucky enough to reach stage four but not get discovered until after surgery (such as bowel cancer), then this can sometimes be cured depending on where the cancer was located (only 1% of patients made it to stage 4).
How long on average does someone die of cancer:-
The Bot has chosen the most common of these four. The overall number of people who will get cancer during their lifetime is about one in two. However, if you mean how long do people usually survive after getting diagnosed with cancer, then that depends on where in your body it started; not all types of cancers are equally treatable.
A good way to work out your prognosis (how long you might live) is for you to look up what stage (level of severity) each of your symptoms falls under using our Symptoms Chart. If there is more than one level listed next to your symptom(s), choose which applies to you.
what is stage 4 cancer of the liver:
The liver is divided into eight anatomic regions (regions refer to the anatomical location and organ boundaries). The four regions that make up the right lobe are anterior segmental (one region), lateral segmental, caudate, and quadrate lobes. The left lobe consists of medial segmental, lateral segmental, ventral caudate, and quadrate lobes.
Three kinds of tumors are found in the liver. These are hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and metastatic lesions.
The treatment for each of these varies greatly depending on their severity. Cholangiocarcinomas can be treated surgically by removing part or all of the tumor and surrounding tissues. Surgery can also be done to treat metastatic lesions, but it is usually used when the tumor has been found early and not spread too far.
The prognosis depends on where in the liver your cancer started and how much it has spread (if at all). Unfortunately, cholangiocarcinomas are one of the cancers that tend to grow quickly and often spread before you know you have it; this makes treatment more difficult. When diagnosed with stage four (4) cholangiocarcinoma, your doctor would give you about six months to live without treatment. With treatment, it could be 6 years or more depending on the severity of the symptoms and how well they respond outside of surgery.
how long does it take for stage 3 cancer to metastasize:
It usually takes weeks or months for cancers to spread. It can happen sooner if the cancer is aggressive or spreads quickly, but this is not always the case. Cancer itself cannot be seen with the naked eye; however, sometimes cancer cells are found in other locations which can be an indicator that they have begun to spread. Unfortunately, it is also possible that these cells are present for many years before they are detected by a blood test or x-ray scan.
what is stage 4 cancer in the brain:
Cancer in the brain is called glioma. There are four different kinds of gliomas, and they depend on which part(s) of the brain it has spread to:
1.) Anaplastic Astrocytoma:
this is the most common type relevant to adults. It grows slowly but can spread into nearby tissue or other parts of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
2.) Oligodendroglioma:
these grow slowly but can also move into surrounding areas. They tend to affect older people than astrocytomas do, who happen to be more often female than male, although it affects all ages equally.
3.) Ependymoma:
this type tends to be formed by cells that line the ventricles (fluid-filled spaces) in the brain and spinal cord. It doesn’t usually spread to other parts of the nervous system, but it can grow into nearby tissue and bone.
4.) Glioblastoma:
this is by far the most common type of brain cancer; roughly half of all malignant (cancerous) brain tumors are glioblastomas. They often happen in adults and affect men more than women; however, these trends vary widely depending on how old you are when you get diagnosed with a glioblastoma.
If you have been diagnosed with stage four (4) glioblastoma, then your doctor would tell you that there is no cure for your cancer. With treatment options available, you may have months to years to live depending on the severity of your symptoms and how well they respond outside of surgery.
However, that is only if cancer has not already spread to other parts of your body. If it has spread, then you are more likely looking at several weeks or months to live without treatment. With treatment, it could be 6-10+ years depending on the severity of your symptoms and how well they respond, and any side effects from treatments/medicine you happen to be taking for that time.