What Are The Symptoms of Frequent Urination?
Symptoms may include:
feeling the need to urinate more often than usual. Urinating more than eight times a day is considered abnormal. Urinating small amounts at each trip to the bathroom has trouble starting your urine stream dribbling after urinating.
Near-continuous or intermittent urination during sleep passing urine that smells bad blood in the urine, which could be a sign of an infection pain or burning when urinating lower abdominal pain incontinence, which means leakage of urine
What are the causes of frequent urination?
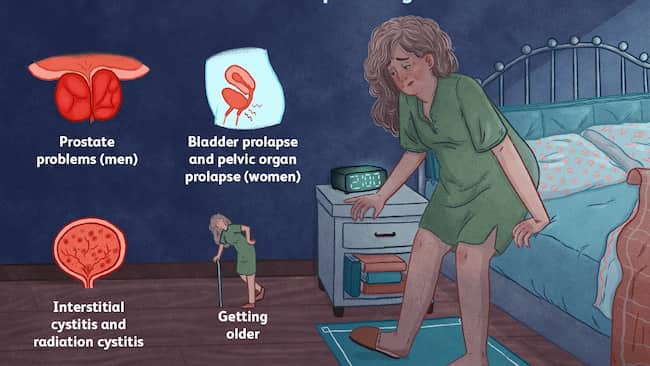
There are many causes for the increased frequency of urination. The most common cause is superficial overactive bladder, which means muscle squeezes too often or too hard. Other causes include urinary tract infections, enlarged prostate in men, diabetes, nerve disorders, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease.
How does an individual prevent frequent urination?
To prevent frequent urination, one needs to follow a healthy lifestyle by maintaining an ideal weight and drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Only take part in activities that are suited to your physical condition. Do not put unnecessary stress on your body when exercising or doing heavy work around the house. Avoid using diuretics, which might lead to dehydration.
What are the treatments for frequent urination?
If an individual is experiencing symptoms of frequent urination, they should first see a doctor diagnose the underlying cause.
Medications are often used to treat overactive bladder symptoms. If the infection is the cause, then antibiotics are used. Other drugs may be prescribed based on your condition. Home remedies include avoiding caffeine, alcohol, acidic beverages, and spicy foods that might irritate or inflame your bladder.
How can you prevent frequent urination?
An individual can prevent frequent urination by maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise routine. Drinks plenty of water throughout the day, so it would be easier to pass urine without straining themselves too much. It will also help in preventing constipation and urinary tract infection. Avoid taking diuretics, caffeine, or alcohol, which would make you go to the bathroom more frequently than usual.
How to stop frequent urination:
Frequent urination is an uncomfortable and annoying problem. It also poses a critical health risk, affecting nerves, muscles, bladder, and kidneys. Here’s how you can stop frequent urination:
Dehydration:
Feeling thirsty and going to the loo frequently could result from dehydration. When we’re dehydrated, our bodies lose fluid more quickly than we can take it on. One way or another, that liquid has to go – either by sweat or urine; so if you aren’t drinking enough water, your body will try to get rid of whatever liquid your cells contain naturally through peeing. In short, drink more water!
You are eating foods with high water content, e.gumbers, celery sticks, etc.
Not drinking enough water throughout the day is one of the leading causes of frequent urination. Make sure you’re staying hydrated by drinking at least eight glasses of water a day. It’s also important to avoid caffeinated beverages, which act as diuretics and make you urinate more frequently.
Alcohol intake:
While alcoholic beverages contain a lot of water, they can keep you well hydrated. Alcohol is a diuretic that makes your body expel more fluids than it takes in. Drinking too much alcohol will not only make you need to urinate frequently but could leave you dehydrated as well.
what causes frequent urination in females:
In addition to staying hydrated, several other lifestyle habits can affect how often you need to go. Eating spicy foods and caffeine, for example, will both leave you running to the bathroom more often than usual.
Alcohol intake:
While alcoholic beverages contain a lot of water, they can keep you well hydrated. Alcohol is a diuretic that makes your body expel more fluids than it takes in. Drinking too much alcohol will not only make you need to urinate frequently but could leave you dehydrated as well.
Several causes:
1) Urinary tract infection (UTI):
The symptoms of UTIs include burning or stinging while urinating and having an intense urge to use the toilet. Some people with UTIs feel like they always need to pee.
2) Cancer of the bladder or prostate:
This is less common than a UTI, but some patients frequently report urinating even if their urinary tract is clean. Patients with cancer will typically experience extreme fatigue and blood in their urine.
3) Diabetes:
People with diabetes can develop neuropathy (nerve damage) which affects the nerves that control the bladder muscles; this can cause frequent urination at night or while resting. They may also be thirsty all the time due to high blood sugar levels, which may be confused for being under-hydrated from drinking too little water.
4) Overactive bladder:
OAB occurs when the pelvic floor muscles tighten up, which causes the bladder to contract. As a result, the urge to urinate becomes challenging to control. This can be highly distressing and disruptive at night, as it often leads patients to “wake up” to use the toilet multiple times.
5) Medications:
Many over-the-counter medications can cause frequent urination or an intense need to go, including allergy drugs, herbal remedies, diuretics, antihistamines, blood pressure medications, and antidepressants.
6) Lifestyle factors:
The intensity of nervousness or anxiety affects how much we need to go pee; people who are frequently stressed out will likely have problems with an overly active bladder. Additionally, drinking caffeinated beverages makes you urinate more, a diuretic.
7) Alcohol intake:
While alcoholic beverages contain a lot of water, they can keep you well hydrated. Alcohol is a diuretic that makes your body expel more fluids than it takes in. Drinking too much alcohol will not only make you need to urinate frequently but could leave you dehydrated as well.
8) Pregnancy:
It varies among individuals how often women experience urinary frequency during pregnancy. Frequent urination typically decreases after giving birth, though some women continue to have an increased urge to go throughout their pregnancies and for months following delivery.
medication to stop frequent urination:
Certain medications can cause patients to urinate more often.
1) Antibiotics:
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and norfloxacin (Noroxin) increase your chance of experiencing an overactive bladder, which could lead to the urgent need to use the bathroom.
2) Blood pressure-lowering drugs:
Diuretics, also known as water pills, are used to lower blood pressure in people with hypertension; they increase blood flow through the kidneys while reducing sodium levels in your body.
You may find yourself running to the bathroom more frequently than usual during this process. If you’re already dealing with frequent urination regularly, trying an alternative antihypertensive medication that doesn’t have this side effect may be helpful.
3) Antidepressants:
Bupropion (Wellbutrin), citalopram, desvenlafaxine, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, and sertraline are antidepressants that increase the amount of urine your body produces. This can lead to frequent urination at night while you’re sleeping or when you’re taking a nap.
4) Antihistamines:
Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine used to reduce symptoms of allergy attacks, including itching, sneezing, and watery eyes; it also decreases bladder muscle contractions. While taking this medication for allergies can prevent you from experiencing severe complications, you could end up frequently waking during the night to use the bathroom.
5) Antispasmodics:
Although antispasmodic medication improves bladder function in people who suffer from overactive bladder (OAB), it could also lead to needing to urinate more often.
6) Diuretics:
A diuretic causes your body to expel more fluids than it takes in. However, they’re widely available at most pharmacies and can offer a solution for those suffering from high blood pressure or edema. They may increase your urge to urinate too frequently. This medicine mustn’t interfere with other medications you might be taking as well. If your doctor prescribes a diuretic, make sure it’s compatible with any other medications or supplements you may take.
7) Heartburn drugs: Proton pump inhibitors (PPI):
PPI is the most common type of medication used to treat heartburn. At the same time, they can provide long-lasting relief. PPIs like omeprazole (Prilosec), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and esomeprazole (Nexium) increase your chances of having overactive bladder problems.