How is Leukemia Detected?
What is leukemia?
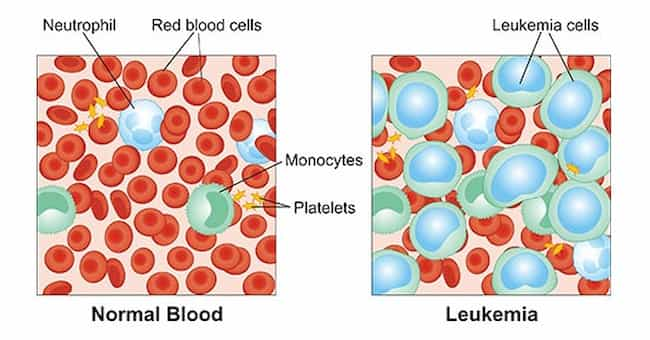
Leukemia or leukosis is a type of cancer that affects the bone marrow. It causes high numbers of abnormal white blood cells to be produced in the body. The disease can affect any animal, mainly dogs, cats, cows, and horses.
The first suspected cases were those by Sir James Paget in 1849. He described a condition in cows, but it wasn’t until 1901 that it was first diagnosed by Drs Tadeusz Borowicz and Rudolf von Kremer in humans.
To detect this disease, there are many methods used. They include:
– Blood tests
– Bone marrow biopsy
– Bone marrow aspirate
– Whole-body radiographs
– Ultrasonography
– CT scan or MRI scan
– X-ray
– Radioactive scans
– MIBG scans
– Radionuclide bone scan
These tests are used to diagnose the presence of leukemia and for its differentiation from other diseases such as lymphoma. These diagnostic methods help doctors decide on the appropriate treatment options for their patients. These tests can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and for early detection of recurrence.
Leukemia can be diagnosed by:
– A complete blood count (CBC)
This test involves looking at a sample of cells from the dog or cat’s blood under a microscope. The number and shape of the white blood cells are examined in detail, and their size, shape, and color are noted. A unique chemical dye is used that stains the nuclei of white blood cells pink or purple, allowing them to be seen more clearly under a microscope.
symptoms of blood cancer in females:
fatigue, pale skin, weight loss, fever or night sweats, bone pain, and anemia
symptoms of blood cancer in males:
swelling in the arms or legs, tiredness, problems with balance, and a high temperature.
Symptoms of blood cancer can happen in various parts of the body. Sometimes, the symptoms are very similar to other diseases or conditions. It would be best if you told your doctor how you feel.
Treatments for blood cancer are different depending on what type of blood cancer. These treatments may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or specific biological therapies.
The lymph nodes are small round things located throughout the body underneath the skin. They help produce antibodies to fight disease.
Symptoms of swollen lymph nodes include painless swellings that can be felt through your skin or pressed against it. You may also have swelling in the groin area, under an arm, or around a fingernail.
How is leukemia treated:
A type of stem cell transplant called an autologous stem cell transplant
Getting chemotherapy followed by a stem cell transplant.
How are leukemias treated:
There are two types of leukemia; both are treated using medications, sometimes with radiation therapy or other treatments depending on the type and severity of your cancer. These include:
You have also been diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Sensitive means sudden onset or rapidly spreading to another part of the body. Myeloid means that your cancer cells grow in the bone marrow, making the three major blood cell lineages- red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
If you would like to learn more about this disease, browse through our website, where you will find a wide range of related articles. You can also contact us to help you with any questions, concerns, or helpful information you may need.
Symptoms of acute lymphoblastic leukemia include:
fever, sore throat, chills, and extreme fatigue may last for several days before the cancer is diagnosed. Symptoms in later stages of the disease may include weight loss or being more tired than usual; pale skin; bone pain; bleeding or bruising easily; swollen lymph nodes; frequent infections such as sinus or ear infections; numbness or weakness on one side of the body (Hodgkin’s disease); enlarged liver and spleen (SLL); testicles (or fertility problems for women).
what causes leukemia:
We do not know what causes leukemia. We think it is a combination of both genetic and environmental factors that lead to changes in a person’s genes, making the body produce cancer cells. Sometimes, but not always, these gene mutations can be passed from parent to child.
Sometimes specific risk factors may increase your chance of getting this disease, such as exposure to radiation or chemotherapy treatment for other cancers- an inherited disorder or trait called familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), which means you have a greater chance of developing bowel cancer- being exposed to certain chemicals at work- being exposed to benzene at home or in the workplace.- chronic inflammation in the colon like Crohn’s disease (a type of inflammatory bowel disease)- your immune system not working correctly, which would make you more susceptible to infection.
How is leukemia diagnosed:
Sometimes the symptoms of leukemia are so similar to other illnesses that it can be difficult for a doctor to diagnose. A diagnosis usually begins with a visit to your family doctor or general practitioner, where they will ask questions about your illness and do an examination.
Once this has been done, your doctor may refer you to see one of the following specialists:-a hematologist (blood specialist)if there is blood in your body-an an oncologist (cancer specialist) if the abnormal cells have begun multiplying appear cancerous.
-a bone marrow expert, if you have pain that spreads through both arms.-Doctors, may also need several tests like x-ray, ultrasound, or MRI that can help them to diagnose leukemia.
How do you get leukemia:
We do not know how people get leukemia. Most people diagnosed with this disease have no known risk factors, which means they have not inherited any genes or traits from their family that might suggest an increased chance of developing the disease.
It is often said that our lifestyle habits and probability risks determine the chance of being diagnosed with cancer- some cases are due to exposure to chemicals at work or in the environment- radiation treatment for other cancers – childhood infections like chickenpox or measles may play a role in leukemia later on in life if they have not been adequately treated – certain inherited conditions or traits can increase the risk of developing cancer in general- from parents to children.
symptoms of leukemia:
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) can be identified by the presence of 20% or more immature cells in the blood and bone marrow. Even at this early stage, ALL is highly aggressive, spreading quickly and aggressively through the body.
Symptoms experienced by patients with ALL include fatigue, pale skin, easy bruising or bleeding, frequent infections including pneumonia or bladder infections, swollen lymph nodes throughout the body often accompanied by a fever, weight loss despite an increased appetite, pain where bones meet such as in the back of legs when walking up stairs or discomfort in arms when lifting something heavy all indicating a low blood count most commonly white blood cells.
Some additional symptoms may also present themselves, which may indicate a different type of blood cancer is present instead of ALL, such as a patient with T-cell leukemia having a generalized swelling in the body from increased fluid retention or patients with myeloid leukemia experiencing night sweats and unexplained fevers.
How does leukemia affect you:
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) attacks immature white blood cells called lymphocytes, part of the body’s immune system. White blood cells are needed to fight infections. Because ALL affects rapidly dividing cells, antibiotics are ineffective because they attack bacteria, not cancer cells. Therefore, chemotherapy drugs must be used to kill the leukemic cells.
The chemotherapy drugs can cause many side effects that may last for months or years after treatment has ended, including nausea/vomiting, loss of appetite, tiredness or fatigue, mouth sores, infertility (which may be permanent), and secondary cancers.