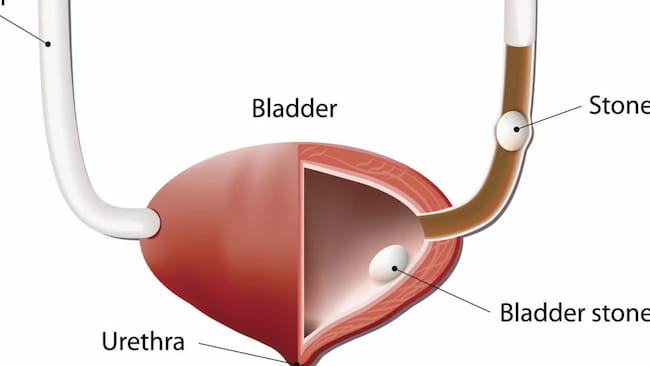
Bladder Stone Symptoms
Frequent urge to pass urine.
Pain when passing urine.
They pass small amounts of urine at a time or get up during the night to pass urine.
Blood in the urine (haematuria). This is not common unless there has been an infection that has caused inflammation (cystitis) and may cause blood to leak into the urine. In men, bladder stones can obstruct urine flow from the kidney downwards through the ureters as it enters each bladder.
This causes a backup of fluid that leads to dilatation, or widening, of the renal pelvis and calyces on X-ray. The blocked ureter causes a ‘back pressure’ to rise into the kidney and then damages it by restricting urine outflow. Damage to the kidney may be permanent.
Bladder stone treatment:
Most stones are small enough to be passed in the urine. This is known as ‘non-operative management’ because no operation is required. The patient drinks water or other fluids to make more urine, and the stone passes out of the body in the urine stream.
A high fluid intake (at least 2 liters a day) should continue for about a week after a stone has passed to ensure no fragments are left behind in the bladder. It can help to urinate while sitting on a warm bath, with a hot water bottle over your stomach area. If there is a lot of blood in the urine, fluid intake should be reduced to about 1 liter a day.
If the stone has not passed within a week, you should see your doctor. Other treatments may be needed to break up and remove a large rock, or an infection could have developed around it called a ‘Staghorn calculus.’ The disease is more likely if bleeding from the urethra or urinary obstruction. In these cases, hospital admission for intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
The risks of developing bladder stones include recurring infections of the bladder (recurrent cystitis), metabolic conditions such as gut absorption problems in children with cerebral palsy that lead to recurrent urinary tract infections, obstructions due to congenital disabilities, anatomical abnormalities, or neurogenic bladder where patients have no sensation or control over their bladders.
Bladder stone symptoms in children:
Pain or burning when passing urine.
The pain often stops when the child is lying down.
A persistent urge to pass urine.
The child may try to pass urine very frequently or get up at night because of the pain.
They are passing small amounts of urine at a time, passing it slowly, having accidents (in incontinent children), or wetting themselves more often than usual.
Bladder stone symptoms in adults:
Adult bladder stones usually cause blood in the urine but can also cause infection, high temperature, and pain when passing urine. The patient has severe lower abdominal pains, which worsen when they pass water, stand up, or cough.
Sometimes incontinence occurs if there is complete obstruction of the ureter by large stones or sludge. Attempts should be made to treat patients with urinary tract infections as soon as possible because of the increased risk of further stone formation.
Bladder stone treatment in adults:
Depending on the size and number of stones, different treatments are available. Some of these include lithotripsy, where sound waves are used to break down bladder stones to be passed naturally. If the stones do not pass out, then surgery is required.
This breaking up or crushing the stone for removal is typically faster than allowing them to pass spontaneously but usually requires general anesthesia. A newer technique is known as “Ureteroscopy” has also been used successfully to remove large bladder stones, which cannot be treated with other methods. An instrument is inserted through the urethra (urine tube) into the bladder to locate and eventually remove the stone.
This procedure has reduced the need for complex surgery that involves opening up the abdomen, potentially avoids all the risks associated with major surgery, and provides a much quicker recovery period.
Female bladder stones symptoms:
Female bladder stones are very much similar to male bladder stones. The only difference is that female bladder stone develops in the urinary bladder of the females only, whereas male kidney stones develop in kidneys.
Female bladder stones also affect both sexes equally, i.e., males and females have equal chances to get involved by these types of rocks. Females who suffer from obesity, diabetes, or hypertension are more likely to be affected by this disease than other women.
The most common symptom of female urinary tract infection is pain during urination, which means there is some obstruction in urine flow inside the vagina. It is mainly caused due to concentration of bacteria at one place, which leads to the formation of crystals resulting in Urinary Tract Infection (UTI).
bladder stones vs. kidney stones:
Bladder stones are formed within the urinary bladder, whereas kidney stones develop in the kidneys.
There is a slight difference between these two types of stone compared to their formation process, symptoms, and treatment. Bladder stones are small, whereas kidney stones are pretty significant.
Symptoms of both types of stones vary from person to person, depending on the severity of infection or disease. Treatment for female bladder stones is different than that for female kidney stones. Whereas some medicines can cure one type of stone, other medicine works for another kind only. Some natural remedies can quickly cure two types of rocks at home with no side effects.
Natural Remedies for Female Kidney Stones:
1.) Watermelon:
You will be surprised by knowing this, but watermelon is one of the most effective natural remedies for female kidney stones. Watermelon is extremely good at dissolving those big, painful, and irritating stones from your organ. It contains a high amount of citrulline that helps break down the tiny crystals into uric acid, which can be quickly passed out from your system. You can use this fruit juice daily to prevent further stone formation.
2.) Lemon:
Lemon also contains a high amount of citric acid, which provides similar benefits as watermelon does, i.e., it breaks down the crystals or tiny particles of calcium oxalate or cystine considerably and provides an easy way out of your body. Drinking lemon juice daily will help you fight those harmful stones without visiting the doctor again and again.
3.) Apple Cider Vinegar:
It has been found that apple cider vinegar has a fantastic effect on your bladder stones. It works by dissolving the solid crystals of calcium oxalate or cystine, which are among the most common types of urinary tract stone-based infections in women.
These small but dangerous stones cause significant obstruction to urine flow inside your bladder, making you feel extremely painful during urination. This can be easily prevented with apple cider vinegar because it contains acetic acid, which breaks down the solid particles into a liquid that can pass through quite quickly without causing any pain or discomfort to you.
4.) Ginger:
If you suffer from recurring kidney stones, then ginger is what you should rely on as it is constructive in fighting off the pain and discomfort caused due to stones. Ginger has a lot of anti-inflammatory properties that work wonders at treating your body without causing any side effects. Along with its pain-killing properties, it also contains many antioxidants and anti-bacterial elements that help fight infection inside the urinary tract system.
These natural remedies for female kidney stones work best when combined to provide faster relief. You can buy all these items from your nearby grocery store to make a completely natural remedy for breaking down those harmful bladder stones.
Make sure to drink plenty of water and consume such food items daily to get rid of this agony once and for all, don’t forget to share your experience in the comments section below.
kidney stone stuck in bladder symptoms:-
Kidney stones can be pretty painful and very difficult to pass. Stones that get stuck in the urinary tract somewhere between the kidney and bladder or just in the urethra can cause severe pain and should be removed as soon as possible by a doctor to prevent emergency surgery.
A stone is considered stuck if it will not move no matter how much you try. The most important thing with any stone is making sure they are small enough to pass on their own so avoiding becoming an emergency where surgery may become necessary.
Symptoms of having one stuck in your body include sharp pain in the lower abdominal area followed by vomiting, fever, chills, nausea, and urination trouble, including either passing very little urine when trying or nothing at all, pain when urinating, and extreme lower back pain.
Sometimes it can be hard to tell the difference between a kidney stone that is stuck in your bladder versus just being one that is lodged in your urethra or urinary tract system. Your doctor should always check any pain in this area so they can determine if you have a trapped stone or something else, such as an STD.