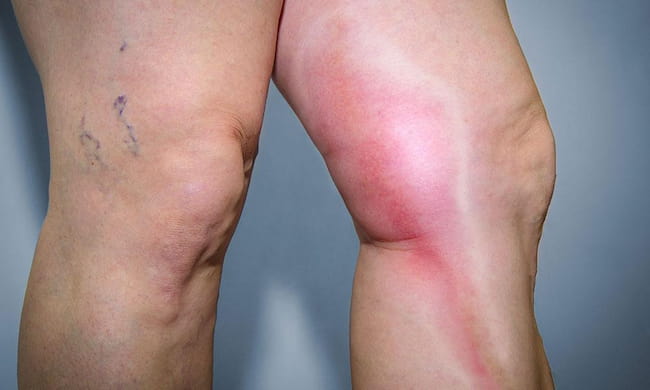
Thrombophlebitis
A potentially dangerous vein inflammation, usually in the leg, is caused by a blood clot.
Deep vein thrombosis:- A blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins in your body, often in your leg.
When a blood clot lodges in a vein, it can block blood flow and cause swelling and pain. The condition is called thrombophlebitis. If the clot breaks free and travels to your lungs, it’s called a pulmonary embolism and can be deadly.
The risk factors and causes of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism are similar.
They include:
• A previous blood clot in a deep leg vein or elsewhere (You’re at increased risk if you have a history of blood clots in your family.)
• Obesity
• Sitting still for long periods, such as during a long airplane flight or after surgery
• Broken bones, such as those from severe trauma, significant surgeries, accidents, or severe burns
Other risk factors may include:
• Age – Although people of any age can develop DVT and PE, these conditions most commonly affect adults over 60 years old. People who take birth control pills may also face an increased risk. Women who are pregnant or recently gave birth are also at risk.
• Cancer – People with cancer may have a higher risk of DVT and PE. This is because cancer can damage the blood vessels and make forming a blood clot more likely.
• Smoking
• Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, kidney failure, or diabetes
If you have any of these risk factors, it’s essential to take steps to lower your risk of developing a blood clot.
These steps may include:
• Quitting smoking
• Exercising regularly
• Taking medications that help thin your blood (blood-thinning medications)
If you think you may have a blood clot, see your doctor immediately. Treatment options include taking blood-thinning medications or, in some cases, surgery.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are two dangerous conditions when a blood clot forms in a vein. DVT is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins in your body, often in your leg. PE is a blood clot that breaks free and travels to your lungs. Both conditions can be deadly.
Symptoms of DVT and PE vary, but common symptoms include:
• Swelling in one leg
• Severe pain or tenderness in your leg
• Redness or warmth over the affected area
• Warmth extending beyond the affected region, either up your leg or to your abdomen, chest, arm, or groin area. This may signify that the clot has traveled from a deep vein to a smaller vein and then to an artery to your lungs. If this happens, you have PE. When PE occurs without any symptoms of DVT beforehand, it’s called “silent” PE because you might not know right away that you have a PE.
Thrombophlebitis treatment:
thrombophlebitis is a term used when an inflammation of a vein becomes infected. Thrombophlebitis most commonly occurs in the lower extremities, usually in the leg or foot near the groin, knee, or thigh areas.
A blood clot inside the vein wall may cause permanent damage to the affected area by cutting off its average circulation, resulting in pain and suffering for millions of people worldwide suffering from thrombophlebitis every day.
The treatment for this condition is being given many misconceptions about its causes and effects that are not true at all., although it must be admitted that one has to live with this disease because there is no cure for it, we can easily manage our life in a way that will live in the same place and sleep in the same bed.
Thrombophlebitis causes:
There are several causes of thrombophlebitis, including the following:
• Sitting or standing for long periods. This increases the risk of a blood clot forming in the veins of the leg.
• Injury to the vein. This may occur from a sharp object, surgery, or other trauma.
• Use of birth control pills or hormone therapy. These medications can increase the risk of developing a blood clot.
• Cancer. Some forms of cancer increase the risk of developing a blood clot.
Thrombophlebitis symptoms:
The most common symptoms of thrombophlebitis include:
•elling and pain along the vein that is usually worse with movement.
•redness, swelling along the affected vein.
• the skin over the affected area may also appear shiny or bruised.
•ight-headedness or shortness of breath in people with blood clots in large veins (deep vein thrombosis).
Thrombophlebitis treatment:
The treatment for thrombophlebitis depends on the cause of the condition. Treatment may include the following:
•Wearing compression stockings. These stockings help to keep blood flowing through the veins.
•Taking medications to thin the blood, such as heparin or warfarin (Coumadin).
•In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the clot.
Thrombophlebitis self-care:
You can do several things to help relieve symptoms and improve your overall health while living with thrombophlebitis.
•Rest as much as possible. This will help reduce swelling and pain.
•Keep the affected area elevated. This will help reduce swelling.
•Avoid sitting or standing for long periods.
•Wear compression stockings.
•Move around as much as possible.
This will help keep the blood flowing through the veins.
•Drink plenty of fluids to help keep the blood flowing smoothly.
•Eat a healthy diet, including plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Thrombophlebitis prognosis:
The long-term prognosis for thrombophlebitis depends on the cause of the condition. In most cases, thrombophlebitis can be treated effectively and not cause any long-term problems. However, thrombophlebitis can lead to more severe diseases, such as deep vein thrombosis in some cases.
Living with thrombophlebitis can be difficult, but there are several things you can do to help relieve symptoms and improve your overall health. Rest as much as possible, keep the affected area elevated, avoid sitting or standing for long periods, and wear compression stockings. In addition, move around as much as possible to keep the blood flowing through the veins.
Drink plenty of fluids and eat a healthy diet, including plenty of fruits and vegetables. In most cases, thrombophlebitis can be treated effectively and not cause any long-term problems. However, thrombophlebitis can lead to a more severe condition, such as deep vein thrombosis in some instances.
Thrombophlebitis vs. thrombosis:
Thrombophlebitis and thrombosis are two conditions that cause blood clots to form in the veins.
A thrombus, or blood clot, forms when damaged blood vessels allow blood to pool and clot. Thrombophlebitis occurs when a vein is inflamed due to this pooled-up blood. When a person has either of these conditions, blood clots can form within the affected vein(s) if the inflammation remains untreated for too long.
Symptoms of both diseases are similar enough that they can be mistaken for one another by people who are not medical professionals. However, several critical differences between thrombophlebitis vs. thrombosis make it essential to know which condition you are experiencing.
The primary difference between the two diseases is that thrombophlebitis is localized, while thrombosis is more severe and potentially life-threatening.
Thrombus formation in thrombophlebitis usually occurs near the skin’s surface, while blood clots in thrombosis can form anywhere in the body, including deep within the veins.
Thrombophlebitis is also less severe than thrombosis and typically responds well to treatment. However, thrombus formation in the thrombophlebitis can lead to deep vein thrombosis if left untreated. Deep vein thrombosis is associated with several complications, including pulmonary embolism.
People experiencing symptoms of either condition should contact their health care provider immediately. Thrombophlebitis does not typically require hospitalization or surgery. Still, people experiencing symptoms of deep vein thrombosis may need these interventions to prevent long-term problems related to the formation of blood clots within the veins.
Thrombophlebitis symptoms:
Thrombophlebitis usually occurs in the superficial veins close to the skin’s surface. Symptoms of thrombophlebitis can include:
•Swelling – due to inflammation
•Redness of the affected area
•Continued pain or tenderness at the affected site, even after the inflamed blood vessel has been injected with a local anesthetic.
Thrombophlebitis causes:
inflammation of a vein is called thrombophlebitis; thrombus formation causes inflammation. The risk factors for developing thrombosis depend on which part of the body is affected. Factors that increase your chance of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) include:
•Obesity
•Prolonged immobility, especially in the air or on an airplane
•Smoking
•Age is older than 60 years in the general population. The risk for people with known clotting conditions or who already had a DVT is much higher.
Thrombophlebitis symptoms:
Thrombophlebitis usually occurs in the superficial veins close to the skin’s surface. Symptoms of thrombophlebitis can include:
•Swelling – due to inflammation
•Redness of the affected area
•Continued pain or tenderness at the affected site, even after the inflamed blood vessel has been injected with a local anesthetic.
Thrombophlebitis treatment cream:
If you are looking for a way to minimize the pain associated with thrombophlebitis, then using a cream that contains lidocaine may help. Creams containing this ingredient will provide temporary relief by blocking out pain signals from nerve endings.
The cream does not cure the inflammation, but it can reduce the discomfort caused by thrombophlebitis. This allows your body’s natural healing capabilities to go about their business without interference and helps you to get back to your normal activities.