What is The Treatment for Atherosclerosis?
The treatment for atherosclerosis usually includes medications to lower cholesterol, such as statins, and medications to thin the blood, such as aspirin. Procedures that can help treat atherosclerosis include angioplasty and stenting, which opens up narrowed or blocked arteries, and bypass surgery,
which creates a new route for blood flow around the secured area. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise, are crucial in preventing and treating atherosclerosis.
Can atherosclerosis be reversed?
Although it is not always possible to reverse atherosclerosis completely, lifestyle changes and treatments can help reduce its severity and improve your overall health.
It is essential to make these changes early in the disease process, when your blood vessels are healthy and not severely narrowed. Lifestyle changes can be especially effective for people with risk factors such as high cholesterol or a family history of atherosclerosis.
what is arteriosclerosis:
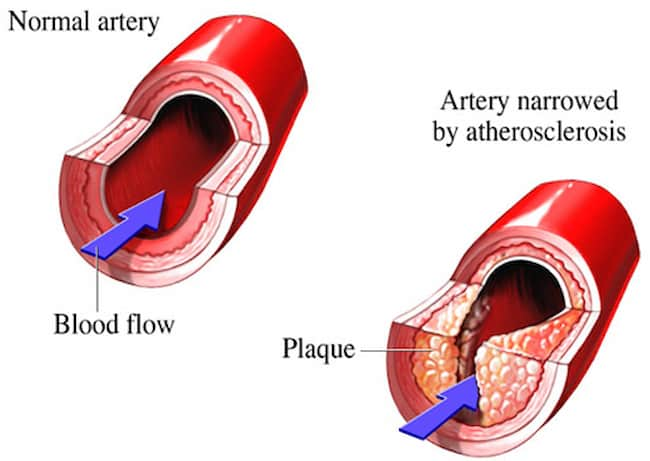
The build-up of fatty deposits and plaque on the inner walls of arteries, called arteriosclerosis, is a severe condition that can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. Arteriosclerosis occurs when the streets become stiff and narrow, making it difficult for blood to flow through them. Over time, this can damage the heart and other organs.
Arteriosclerosis has several risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and diabetes. Treatment for arteriosclerosis usually includes lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, medications to lower blood pressure or cholesterol levels, and surgery in some cases.
what are the symptoms of arteriosclerosis:
The symptoms of arteriosclerosis vary depending on which organs are affected. When the heart is affected, people may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or a heart attack. When the brain is affected, people may experience a stroke. People may experience high blood pressure or kidney failure when the kidneys are affected.
How is arteriosclerosis treated:
Treatment for arteriosclerosis usually includes lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, medications to lower blood pressure or cholesterol levels, and surgery in some cases. Lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing arteriosclerosis or improve the health of people who have it.
Medications can help lower blood pressure or cholesterol levels, which can help reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other problems. Surgery may be necessary to remove plaque from the arteries or repair damage caused by arteriosclerosis.
Prevention:
There are several ways to reduce the risk of developing arteriosclerosis or improve the health of people who have it. Some simple steps include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke, and maintaining a healthy weight. In some cases, medications may also be needed to help reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other problems.
Arteriosclerosis is a severe condition that can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. It occurs when the arteries become stiff and narrow, making it difficult to flow through them. Over time, this can damage the heart and other organs.
Arteriosclerosis has several risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and diabetes. Treatment for arteriosclerosis usually includes lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, medications to lower blood pressure or cholesterol levels, and surgery in some cases.
Atherosclerosis diagnosis:
There are several ways to diagnose arteriosclerosis, including physical exams, imaging tests, and blood tests. Physical exam may include checking the pulse in the arms and legs, listening to the heart and lungs, and examining the skin for signs of poor circulation. Imaging tests such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can provide a detailed image of the arteries. Blood tests can measure levels of cholesterol and other substances that are associated with arteriosclerosis.
There are several ways to diagnose arteriosclerosis, including physical exams, imaging tests, and blood tests. Physical exam may include checking the pulse in the arms and legs, listening to the heart and lungs, and examining the skin for signs of poor circulation.
Imaging tests such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can provide a detailed image of the arteries. Blood tests can measure levels of cholesterol and other substances that are associated with arteriosclerosis.
Arteriosclerosis treatment:
There are several ways to treat arteriosclerosis, including lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, medications to lower blood pressure or cholesterol levels, and surgery in some cases. Lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing arteriosclerosis or improve the health of people who have it.
Medications can help lower blood pressure or cholesterol levels, which can help reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other problems. Surgery may be necessary to remove plaque from the arteries or repair damage caused by arteriosclerosis.
Types of arteriosclerosis:
There are several types of arteriosclerosis, including:
– Atherosclerosis: The most common type, atherosclerosis, occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries. This can block blood flow and lead to heart disease, stroke, and other problems.
– Renal artery stenosis: This type affects the arteries that carry blood to the kidneys. It can cause high blood pressure, kidney failure, and other problems.
– Carotid artery stenosis: This type affects the arteries in the neck that supply blood to the brain. It can lead to a stroke if the blockage is severe.
– Peripheral artery disease: This type affects the arteries in the arms and legs. It can cause pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, and coldness in the legs or arms during exercise.
– Aortic coarctation: This type affects the large blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the body. It can lead to other problems such as high blood pressure.
Arteriosclerosis risk factors:
There are several risk factors for arteriosclerosis, including:
– High cholesterol levels
– Smoking
– Obesity
– Diabetes
Many people don’t know they have stiff and narrow arteries until it causes health problems. But you can lower your risk of arteriosclerosis by eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, quitting smoking, avoiding secondhand smoke, maintaining a healthy weight, and controlling diabetes.
Atherosclerosis of lower extremities treatment:
Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is also known as peripheral arterial disease or PAD. It occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries of the legs, typically those supplying blood to the thighs and calves. This can cause pain or discomfort during exercise.
To diagnose atherosclerosis of lower extremities, a doctor will check for signs of poor circulation by checking your pulse rate and feeling for swollen ankles or feet. You may then have imaging tests that show how well oxygen-rich blood flows throughout your body. Treatments vary depending on whether you need surgery or medication, but lifestyle changes are usually required before any treatment takes place.
Gaining arteriosclerosis:
The more sedentary people, the higher their risk becomes of gaining arteriosclerosis. When people don’t move around, the fatty acids and cholesterol in the blood can slowly accumulate on the artery walls. Smoking, being overweight or obese, eating a poor diet, and having high blood pressure contribute to developing arteriosclerosis.
Arteriosclerosis can develop in any age group but is most common in older adults. As people age, their arteries naturally lose some of their elasticity. This increases the risk of plaque accumulation and the hardening of the arteries.
There are several types of arteriosclerosis, including atherosclerosis, renal artery stenosis, carotid artery stenosis, peripheral artery disease, aortic coarctation. Each type has its own set of symptoms and treatments.
Atherosclerosis of the aorta:
Atherosclerosis of the aorta, also known as aortic sclerosis, is a severe condition leading to a heart attack or stroke. In this type of arteriosclerosis, plaque builds up in the aorta, the large blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the body.
The main symptoms of atherosclerosis of the aorta are chest pain and shortness of breath. These symptoms may be mistaken for other conditions such as angina or heart attack.
To diagnose atherosclerosis of the aorta, your doctor will perform a physical exam and order imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan. Treatment usually involves lifestyle changes and medications to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. If your symptoms are severe, surgery may be needed to remove the plaque and stop blood flow from becoming obstructed again.
Arteriosclerosis causes:
While there is not one single cause for arteriosclerosis, it has been identified that several reasons contribute to this disease process:
– Smoking
– Obesity
– Diabetes
– A family history of the disease increases your risk because you’re more likely to develop it if a relative has had it.
– High cholesterol levels
– Lack of physical activity
– Age (the risk increases as you get older)
Arteriosclerosis can develop in any age group but is most common in older adults. As people age, their arteries naturally lose some of their elasticity, making them more susceptible to plaque accumulation and the hardening of the arteries.
There are several types of arteriosclerosis, including atherosclerosis, renal artery stenosis, carotid artery stenosis, peripheral artery disease, aortic coarctation. Each type has its own set of symptoms and treatments.