Cervical Cancer Symptoms for Girls
1) Changes in the cervix:
Cervical cancer can cause pain or a burning sensation around the vagina. There may be a black, brownish, or watery discharge from the vagina as well as increased vaginal bleeding between periods. The cervical opening may become bigger than usual. As this symptom does not happen often, it might not be noticed easily and so you should see your doctor if any of these symptoms occur during sex with an older partner:
2) Unusual discharge:
This symptom is not caused by cancer but sometimes occurs with it. Girls who have cervical cancer might notice that their normal vaginal discharge changes color or odor to a thick yellow-green or blood-tinged fluid, rather than clear and white. Cytological changes:-
3) Cytological changes:
If a Pap smear reveals any abnormalities, the only way to determine if it is cancerous or not is to go for a colposcopy. A biopsy of the tissue from the cervix will be performed and an experienced doctor can then figure out what kind of treatment you need.
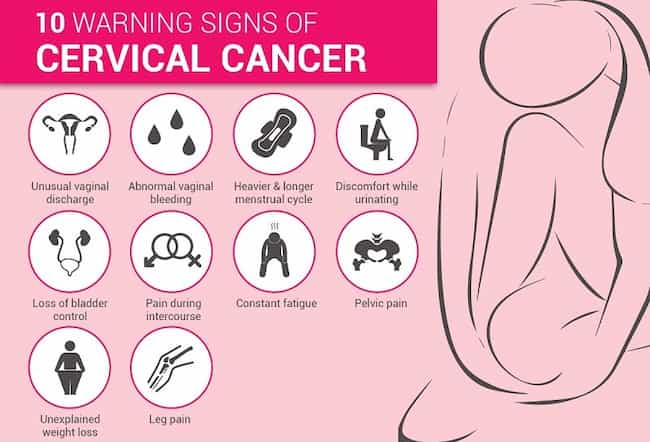
Even though cervical cancer gives no symptoms early on, certain signs indicate that something might be wrong with your cervix. You should contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of these warning signs:
1) Vaginal bleeding in between menstrual periods:
Bleeding in between your periods is not normal. If you are having this kind of bleeding, it means that something is wrong with your cervix or uterus. You should contact your doctor immediately if you notice vaginal bleeding two weeks after the start of a period or before the next one starts up.
2) Pain during sexual intercourse:
If you experience any pain when you attempt to have intercourse, especially when inserting an object into the vagina, this might be a sign that something is wrong with your cervix or uterus. You must go see a doctor if there is any discomfort while inserting tampons into the vagina, for example.
Symptoms of cervical cancer include:
Early signs of cervical cancer may be as you would expect for any infection such as unusual vaginal discharge or bleeding between periods. Bleeding after sex is also a possible symptom.
If cancer has grown bigger, it may cause pain or some other symptoms such as constipation or backache that does not go away with treatment. These symptoms can indicate that a person has a blockage in their bowel or bladder and they will not be caused by treatments for cervical cancer itself.
Cancer often spreads to nearby tissues and lymph nodes before you have any symptoms at all – but this is not always the case. In about 20% of cases, it has already spread to other parts of the body when diagnosed.
Symptoms of advanced cervical cancer include:
Tiredness and breathlessness, due to fluid coming up from the chest into the lungs (pleural effusion). This can make you cough. Nausea and vomiting. Coughing, due to a blockage in a lung artery. Bone pain, caused by changes in the bones where cancer has spread. Changes in bowel habits or bladder habits such as passing black stools or blood in the urine.
Fingers feeling numb or curled up while going to sleep at night (called carpal tunnel syndrome). Swelling of armpit lymph nodes for several weeks if lymph node disease is present throughout the body. In some cases, there may be signs of liver problems, such as yellow skin and swelling of the abdomen that does not disappear when pressed.
Symptoms in children with cancer may include:
Children with a lump in their neck. If you have any of these symptoms, see your doctor so they can check your health and give you the advice to help you feel better. Most cervical cancers are found early when they are still treatable. Cervical screening can discover pre-cancerous changes which means it is easier for the doctors to treat them.
what happens to your body when you have cervical cancer:
When doctors suspect a person has cervical cancer or pre-cancer, they may arrange for them to have a test called a pipeline biopsy. This feels like a normal smear test and involves gently inserting a narrow tube through the vagina up into the womb. The doctor takes some cells from inside the cervix, which is then sent away to look for any signs of cancer under a microscope.
If you have cervical cancer, your doctor will refer you to a specialist center where you can have treatment – this is usually planned as soon as possible but can be delayed if you need other treatments first. Specialist centers use many different treatments for cervical cancer depending on how far the disease has spread at the time of diagnosis and how well your body responds to treatment.
If you are diagnosed with cervical cancer, it is important to know that treatments are available for this type of cancer. You will be referred to a hospital or center where doctors can help you get back to good health again. Talking about your diagnosis and treatment with friends, family, and support groups is important for keeping positive.
cervical cancer urinary symptoms:
If cancer spreads to your bladder, you may start to feel as though you have to go to the toilet more often than usual. This is because the cells from the tumor are blocking off your flow of urine. You will have a feeling that your bladder is not empty even after going to the toilet and find yourself going again very soon afterward.
cervical cancer urinary symptoms:
It can also be painful for patients with advanced cervical cancer, especially when they cough or sneeze. A well-known symptom of terminal cervical cancer is back pain, which will be present in approximately 50% of people. Advanced breast cancers typically cause bone pain.
Bone metastases are associated with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), muscle, joint, and nerve pain. Cervical cancer can also cause a variety of neuropsychological symptoms such as dementia, delirium, seizures, and headaches.