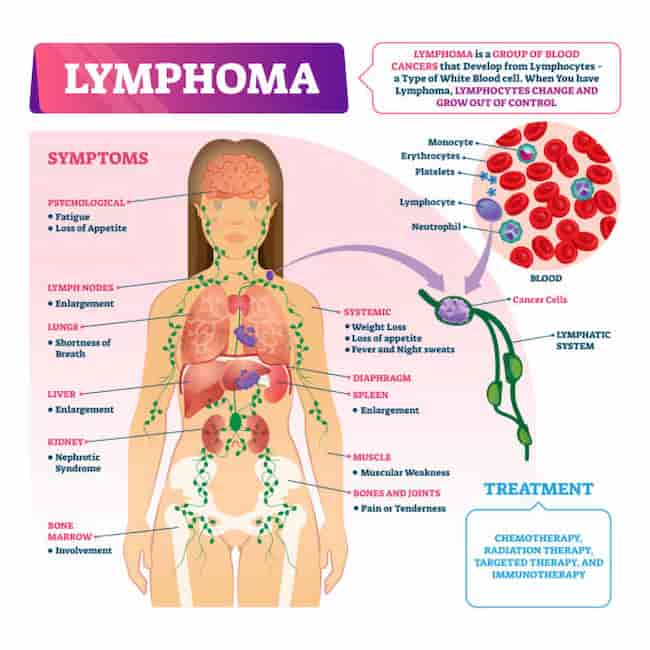
What is Lymphoma?
Lymphoma is a type of cancer formed by a particular type of white blood cell called lymphocytes. It is a blanket term for many types of lymphocyte malignancies that affect the body’s protective system, referred to as the immune system.
Lymphomas are classified according to which type of lymphocytes they originate in B-cell lymphomas (originating in B cells), T-cell, and natural killer (NK) cell lymphomas (originating in T cells or NK cells).
Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma are two subtypes of malignant lymphoma. Lymphoma can be broadly divided into two basic groups, low grade, and high grade. Low grade generally refers to slower-growing cancers while high grade refers to fast-growing cancers.
The World Health Organization (WHO) refers to low-grade lymphomas as indolent lymphomas and the NCI uses the term slow-growing non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
Low Grade or Non-Aggressive Lymphomas:
These are mostly present in older children, adolescents, and young adults. They occur when there is a small number of abnormal immune cells in the circulation that multiply slowly over time causing no harm other than blocking normal blood flow around the body.
They do not spread to distant parts of the body but can cause ‘swelling’ within different organs which can be life-threatening if left untreated. The swelling may occur anywhere in the body including the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, central nervous system (CNS), skin. Many types of low-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas are named after the type of immune cells or tissue where they start.
what is lymphoma cancer:
The term cancer refers to malignant tumors, which can invade adjoining tissue and spread throughout the body. Lymphomas are cancers that originate in lymph nodes or lymphatic tissues. Some form of cancer is responsible for nearly half of all deaths in the United States, including almost 40 percent of all cancer-related deaths. Incidence rates were highest among African Americans (214 per 100,000) followed by whites (158 per 100,000).
Lymphoma is a disease in which cancer starts in the cells of the immune system. The immune system is made up of several types of white blood cells that help fight infection and protect us against disease. White blood cells make up about 25 percent of our weight; there are about three times as many white blood cells as red blood cells in our body.
There are many types of lymphoma; the most common type is called diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Unlike some other types of cancer, like lung cancer, where there is one main type of tumor, DLBCL can start as either a single tumor or as multiple tumors (at different locations). It often goes undetected for several years before it becomes apparent that something is wrong.
Unchecked, this condition can spread to tissues and organs throughout the body and become life-threatening. There may be no early symptoms and signs of the disease and even once these signs and symptoms do develop they may seem similar to those caused by infections or other more benign conditions.
The disease may initially be confined to the lymph nodes, but if left untreated it can spread to other areas of the body causing swelling (edema) and discomfort. Over time, this condition can also cause other signs and symptoms like feeling tired or weak for no reason, night sweats, weight loss, frequent infections including pneumonia or tuberculosis (TB), itching all over your body; bone pain; fever; headaches; swollen glands not in the lymph nodes; lightheadedness; shortness of breath; chest pain caused by fluid around your lungs (pleural effusion).
what causes lymphoma:
The exact cause of lymphoma is not known. However, there are certain risk factors associated with the disease. Some people have a higher risk of developing this condition compared to other people. In addition to the following factors, genes also play a role in your chances of getting lymphoma.
Other possible causes include:
Infections that can cause cancer-like changes in cells throughout the body may increase your chance of developing this disease or make it worse if you already have it.
These infections include coronaviruses (which cause chickenpox and shingles) and hepatitis B and C viruses (which can lead to liver cancer). There is some evidence suggesting that human papillomavirus (HPV), which can cause genital warts and cervical cancer, may also increase your risk for DLBCL.
lymphoma treatment:
One of the important aspects to keep in mind is that there are many treatment options available. Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplantation, or a combination of these treatments.
To give you an idea about what all can be done for lymphoma diagnosis & treatment in India. Mumbai-based Fortis Memorial Research Institute (FMRI) has joined hands with France’s Institut Gustave Roussy (IGR).
IGR will assist FMRI doctors to enhance their expertise and knowledge on the latest treatment options available for blood cancers like multiple myeloma and lymphomas. The institute plans to offer training courses by experts from France who have extensive experience treating cancer patients.
How is lymphoma diagnosed:
Your doctor will look for symptoms that suggest lymphoma, which is usually the sign of infection that is not getting better with time. Other symptoms include swelling in the arms or legs and joint pain.
You may have blood tests to check your white blood cell count, which can be high when you have lymphoma. You may also have a biopsy in which samples of tumor tissue are removed from your body so they can be looked at under a microscope. This is often done when doctors cannot decide whether the symptoms are caused by lymphoma or another condition, such as an infection.
how bad is lymphoma cancer:
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that starts in white blood cells called lymphocytes. When it begins in the “B-cell” form, this type is often more aggressive than other types.
The fact that cells with B-cell origin are often found at the late stage of other lymphomas (and only rarely at the early stage) has led to diagnoses of late-onset diseases (such as DLBCL).
Though the initial stages are usually not fatal if treatment has begun, most people eventually die because they failed to seek medical attention on time or were unable to find an effective treatment for their condition.
symptoms of lymphoma in females:
One in every three women with Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is younger than 50, and the disease occurs in six times more women than men. The most common types of NHL among females are diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular center cell (FCC) NHL, marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenström macroglobulinemia, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic leukemia (CLL/SLL). CLL/SLL is treated differently from the other types because it may not cause symptoms early on.
DLBCL represents 60 to 70 percent of all female NHL cases and is the most common form of lymphoma. This type can be a slow-growing or fast-growing cancer, depending on your age, medical history, the risk for other diseases, and other factors. One to three out of four patients with this disease will have an aggressive form that grows quickly.
The symptoms often include night sweats, fatigue (tiredness), weight loss, an enlarged spleen, or swollen abdomen. Most women are diagnosed when they are in their fifties but younger women are also susceptible to this threat to their health since it can hit anyone at any point in time.