Diagnosis of Muscle Weakness and Atrophy
Muscle weakness and atrophy associated with aging or diseases such as muscular dystrophy may be diagnosed. The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (a disease in which the myelin sheath around neural axons is damaged) can also be made.
The analysis of the electrical properties of the surface muscles may indicate the cause and extent of damage to any particular part of a muscle and aid in determining if surgery will be successful, The electrical activity emanating from a muscle during voluntary contractions is very irregular in nature and this method is not useful for diagnosing neuromuscular disorders associated with smooth muscles such as those found in gastrointestinal tracts.
Diagnosis based on electrical activity is best used when investigating problems related to skeletal muscles. It can provide information that is useful in the assessment of muscle function. For example, if after surgery there is no electrical activity or abnormally low spontaneous electrical activity then this indicates that the muscles are not functional.
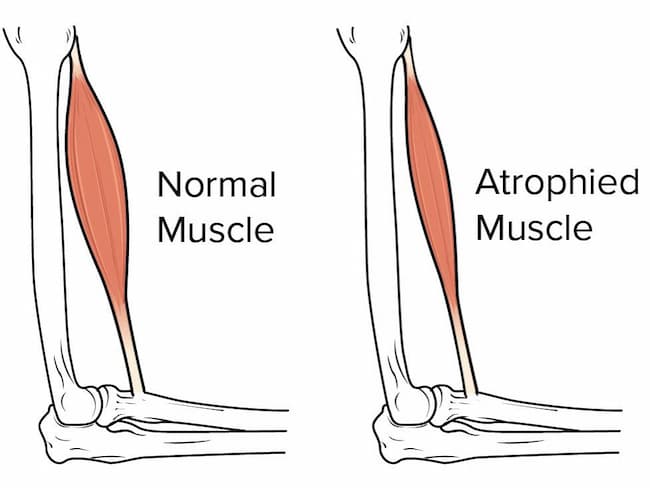
what is muscle atrophy:
Atrophy is a general term for decreased size and strength of muscle and other tissues. It occurs because the body no longer needs all of the cells in these tissues or doesn’t use all of the cells efficiently.
Muscles may become smaller and weaker as part of the aging process, after an illness or injury, or due to inactivity such as during a long hospital stay. The risk of atrophy increases if you don’t move your muscles against gravity (extend them). For example, lying in bed with your legs straight rather than bending your knees can cause atrophy of your leg muscles over time.
Signs and symptoms:
Muscle weakness that starts in one area but spreads to other areas Muscle aches that are often mistaken for the flu Significant loss of weight-related to muscle atrophy
Treatment:
Atrophy caused by inactivity is best treated with active exercise. A physical therapist can suggest ways to do this even if you are confined to bed, using crutches or a walker, or sitting in a chair. A physical therapist also can suggest aids such as elastic bandages or weights that make it easier to use your muscles. Medicines may help strengthen your heart and improve blood flow (see Heart disease treatment ). They might be used along with other treatments (such as casting) if you have broken bones that need healing.
Muscle wasting due to illness or injury needs treatment aimed at that specific illness or injury. For example, bed rest or not moving tends to worsen muscle atrophy caused by hip fractures. Surgery may be used to repair damaged tissue, but it’s rare because most causes of muscle wasting aren’t surgical conditions.
WARNINGS:-
This medicine will only slow muscle loss that is already occurring as part of aging or disease, and should not be considered for use in other circumstances (see Uses ). The long-term effects of tetrabenazine are unknown; therefore, tetrabenazine has not been adequately tested in children younger than 15 years old. Also, tetrabenazine can cause excessive drowsiness leading to falls or accidental injury (see Side Effects ), especially when taken with other medicines that also make you sleepy (such as sedatives, tranquilizers).
Tetrabenazine can cause excessive sleepiness and drowsiness. Avoid getting up too fast from sitting or lying down, especially if you are an older patient. An overdose of tetrabenazine could result in death due to respiratory failure (stopping breathing) or heart failure (when the heart can’t pump blood as it should), which requires immediate medical attention. Do not take any more doses of this medicine until at least 2 hours after your last dose.
Muscle atrophy disease:
Muscle atrophy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Causes of Muscle Atrophy:
There are many causes of muscle atrophy. When the cause is unknown it is commonly called idiopathic. Muscle wasting will occur when there is a loss of skeletal muscle that exceeds the amount that would be expected from normal turnover or loss. This can also happen as a result of immobilization such as what occurs during a cast or due to lack of use such as might occur during a long period in bed following surgery.
It has been reported that up to 30% of people confined to bed for more than 7 days develop significant muscle wasting which can take up to several months before full recovery occurs. There are other etiologies involving hormonal changes or nutritional deficiencies, such as severe burns or any severe injury where significant bleeding and fluid loss occur.
Muscle weakness differential diagnosis:
Difficulty in managing a disease is the main problem in medicine. The allopathic medical science directorate of India has reported many problems related to meningitis treatment, so the real danger of misdiagnosis and wrong management still exists in this high incidence disease like meningitis. A big part of any emergency care involves making sure that you can get an accurate diagnosis of what might be causing someone’s trouble.
You need to know whether it’s something more serious than you’re used to dealing with. This will help decide how much manpower and extra supplies you’ll need. It will also play a big part in determining what type of transport (if any) your patient needs and which hospital or clinic should handle their care.
These are the Five Differential Diagnosis of Meningitis:
1] Bacterial meningitis
2] Viral meningitis
3] Fungal meningitis
4] Protozoan meningitis (caused by parasites)
5] Inflammatory mass lesions that may or may not be related to infectious processes like brain abscess, subdural empyema, subarachnoid hemorrhage, hemorrhagic infarction, etc.
Muscle atrophy in legs:
Proper diagnosis is essential in finding the best treatment for your health condition. The better you understand your health, the easier it will be to make smart decisions about it. Here are some resources that can help you learn more about muscle atrophy in the legs and how to live a healthier life.
Muscle atrophy causes:
Causes of Muscle Atrophy:
There are many causes of muscle atrophy. When the cause is unknown it is commonly called idiopathic. Muscle wasting will occur when there is a loss of skeletal muscle that exceeds the amount that would be expected from normal turnover or loss. This can also happen as a result of immobilization such as what occurs during a cast or due to lack of use such as might occur during a long period in bed following surgery.
It has been reported that up to 30% of people confined to bed for more than 7 days develop significant muscle wasting which can take up to several months before full recovery occurs. There are other etiologies involving hormonal changes or nutritional deficiencies, such as severe burns or any severe injury where significant bleeding and fluid loss occur.