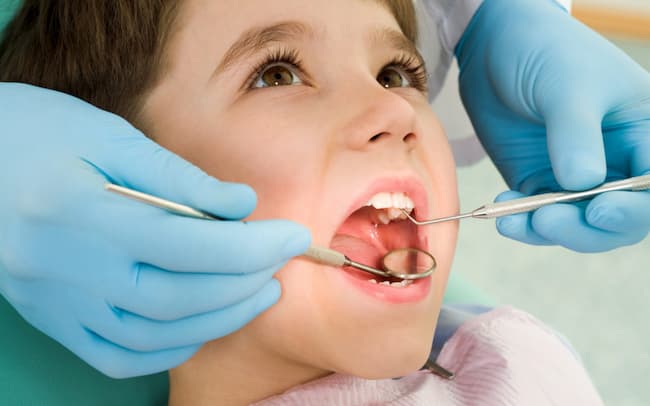
Dental Caries Treatment in Children
Dental caries in children requires special care because their teeth are still growing. In addition, the use of toothpaste and other therapies should be age-appropriate.
The first step in treating dental caries is to remove the decayed material from the tooth. This may be done using some methods such as drilling, laser therapy, or air abrasion. If the decay is extensive, a filling may be required to restore the tooth’s structure and function.
If caries has reached the nerve tissue inside the tooth, root canal treatment may be necessary. This involves removing the nerve tissue and replacing it with a sealant. Crowns or bridges may also be required to restore the tooth’s structure and function.
It is important to note that, as with adults, dental caries in children should be managed by a dentist. Click here for information on how to select a pediatric dentist.
Dental caries treatment in children:
Root canal treatment may be necessary if the decay has reached the nerve tissue inside the tooth. Click here to learn more about root canal treatment. Bridges or crowns may also be required to restore the tooth’s structure and function. Click here to learn more about dental bridge procedures.
Crowns are often used when there is not enough healthy tooth left to hold a filling or a permanent restoration. Click here to learn more about the crown procedure. How do I find out if my child has tooth decay?
How do I know if my child needs dental treatment?
The first step is to establish whether your child has any signs of tooth decay or dental caries. This includes checking that the teeth are developing typically & without any visible damage.
Visible damage may consist of white spots on the surface of the enamel (which can be found using an 8x magnifying mirror) and deep holes in the enamel, called cavities. Toothache or pain during eating is another indicator that your child might need treatment for tooth decay, however, consult a dentist as soon as possible if you suspect tooth decay.
How to treat cavities in baby teeth:
Cavities in baby teeth should be treated with fluoride-containing toothpaste and mouthwash. You can also put a small amount of fluoride gel on the child’s toothbrush. If the cavities are severe, your dentist may need to treat them with a unique filling material.
It is important to remember that baby teeth are essential for chewing and speaking. They also help to hold the space for the permanent teeth. Cavities in baby teeth can sometimes lead to holes in the permanent teeth.
If your child has a cavity, you should take them to the dentist as soon as possible. The sooner the dentist can treat the hole, the minor damage it will cause. Failing to treat a cavity in a baby tooth can lead to pain, infection, and tooth loss.
Cavities in baby teeth should be treated just like cavities in adult teeth. The best way to avoid cavities is to brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride-containing toothpaste and floss once a day. It would help if you also visited your dentist for a checkup every six months.
Cavities are a common problem in both baby teeth and adult teeth. They are caused by bacteria that live in the mouth. These bacteria use sugar from food to produce acids. The acids attack the enamel on the teeth, causing cavities.
When a baby tooth has a cavity, it should be treated with fluoride-containing toothpaste and mouthwash. If the hole is severe, your dentist may need to fill the tooth with a unique filling material. This material stays in the tooth and helps protect it from even more damage.
Sealants can also be used to prevent cavities in baby teeth. Glue is put on the chewing surfaces of the teeth. It keeps out food particles that cause cavities. Sealants are very effective in helping children avoid cavities in their baby teeth. But they only work if you brush after every meal, floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for checkups.
Three-year-old tooth decay treatment:
A child is given anesthesia for treatment of tooth decay in a tooth that has already erupted. The black arrow points to where the pollution is being treated with white fillings.
Tooth decay in baby teeth can be treated in one of two ways. Your dentist may clean out the cavity and put a small amount of fluoride gel on your child’s toothbrush. If it doesn’t get better, your dentist will have to treat the hole with one of several unique filling materials. These materials stay in your child’s teeth and help protect them from even more damage.
Tell your dentist when you set up their first dental appointment if you suspect that your child has milk or saliva allergies. It will be easier for them to treat any cavities if they know about your child’s allergies in advance.
It is important to remember that baby teeth are essential for chewing and speaking. They also help to hold the space for the permanent teeth. Cavities in baby teeth can sometimes lead to holes in the permanent teeth. So it is essential to take your child to the dentist as soon as possible if you think they may have a cavity.
The sooner the dentist can treat the hole, the minor damage it will cause. Failing to treat a cavity in a baby tooth can lead to pain, infection, and tooth loss. So make sure you take your child to see their dentist regularly for checkups even if they don’t have any cavities yet. It’s always better to be safe than sorry.
Cavities in baby teeth should be treated just like cavities in adult teeth. The best way to avoid cavities is to brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride-containing toothpaste and floss once a day.
It would help if you also visited your dentist for a checkup every six months. Make sure that you tell your dentist about any allergies you think your child might have when they set up their first dental appointment.
Signs of the cavity in a toddler:
If you think your child may have a cavity, look for these signs:
– Your child has pain in their tooth.
– Your child has a hole in their tooth.
– Your child’s tooth is discolored.
– Your child’s tooth is sensitive to hot or cold food.
– Your child has terrible taste in their mouth.
– Your child has swollen gums around their tooth.
If your child has any of these symptoms, take them to the dentist as soon as possible for treatment. Cavities can cause pain, infection, and tooth loss if not treated quickly. So make sure you take your child to see their dentist regularly for checkups even if they don’t have any cavities yet.