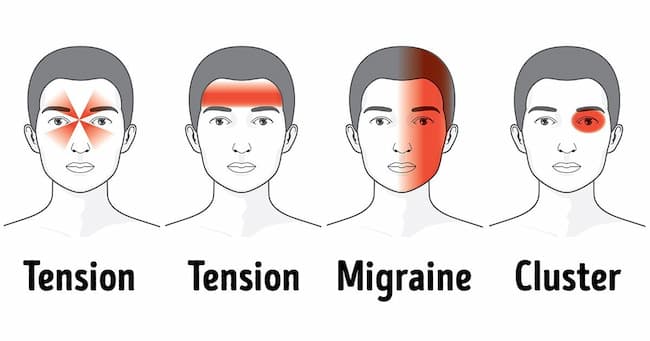
What Are The Causes of Frequent Headaches?
There are many potential causes of frequent headaches, including:
– Stress
– Tension headaches
– Migraines
– Sinus pressure and infections
– Allergies
– Hormonal changes, such as during menstruation
– Reaction to certain foods or drinks
– Lack of sleep or excessive fatigue
– Eyestrain
– Poor posture
If you frequently experience headaches, it’s essential to see your doctor to determine the underlying cause. Once the cause is identified, you can find a treatment that works best for you.
Some common treatments for headaches include:
– Pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
– Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or yoga
– Counseling or therapy to address stress or tension headaches
– Biofeedback training to help relieve sinus pressure and congestion
– Prescription medications specifically for migraines or other types of headaches
– Prescription medications to treat the symptoms of hormonal changes or other medical conditions that may cause frequent headaches
Surgery for more severe cases:
Headaches are a common problem. However, they are not expected. If you’re experiencing frequent headaches, it’s essential to see your doctor as soon as possible so the underlying cause can be found and treated.
Keep in mind that if your doctor prescribes medication, these products do not cure headaches but reduce pain. The work of finding the proper treatment is something you have to commit to yourself.
What are the treatments for chronic migraines?
Medication can help prevent migraines or reduce their severity when they occur, including:
– Triptans (Imitrex, Amerge, Maxalt, Zomig)
– Ergots (Midrin, Cafergot)
– Antinausea medications (Kytril, Norvasc)
– Diuretics that decrease brain swelling (Aldactone, Priceline)
Other options for long term treatment include:
– Amitriptyline to prevent migraines from occurring in the first place. This is an older medication used to treat depression, preventing migraines. There may be side effects, so discuss them with your doctor.
It can cause mood changes and constipation, so if you already suffer from either of these problems, you need to speak with your doctor about this medicine before trying anything else.
– Botox injections. This is a new treatment and is still being studied, but it’s thought to work by paralyzing the muscles around the forehead so they can’t contract and cause pain. It needs to be given every three months, and some people have reported minor side effects such as headache, neck pain, or flu-like symptoms.
Severe headache:
A severe headache can be a sign of a more severe problem. If you experience a severe headache, you should see your doctor to determine the cause. A severe headache may be a sign of:
-A tumor
-A blood clot
-A stroke
-High blood pressure
-An infection
-A head injury
-Dehydration
The most common type of severe headache is a migraine. Migraines are often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
Other types of severe headaches include:
-Cluster headaches
-Sinus headaches
-Tension headaches
If you experience any of the following symptoms along with your headache, seek emergency medical attention:
-Severe pain that doesn’t go away
-Blurred vision
-Numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg
-Difficulty speaking
-Loss of balance or coordination
-Loss of consciousness
causes of headache:
There are several possible causes of headache, including:
-Stress
-Hunger
-Sinusitis
-Head injury
-Tumor
-Brain tumor
Treatments for headache:
Several treatments exist for your headaches. Your doctor may prescribe medications to prevent headaches or lessen their severity. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen (Motrin IB), acetaminophen (Tylenol), and aspirin can provide temporary relief. You should not take over-the-counter drugs if you still have a fever.
If you experience frequent headaches, ask your doctor about preventive treatment options. He may suggest daily exercise, drinking lots of fluids, getting enough sleep, losing weight if necessary, or avoiding certain foods or drinks that trigger headaches. Some people find relief from using a cold pack on their forehead or neck or by massaging their temples.
Causes of migraine in males:
There is no one definitive cause of migraines. Some possible reasons include:
-Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, menstruation, or menopause
-Stress
-Foods or drinks, such as chocolate, red wine, or caffeine
-Sensory stimuli, such as bright lights or strong smells
-Environmental changes, such as high altitudes
-Medical conditions, such as tension headaches, sinus infections, and asthma
Treatments for migraine in males:
Although there is no one definitive cure for migraines, several treatments may help lessen their severity or frequency. Your doctor may prescribe medications to prevent migraines or take them when a migraine occurs.
These medications may include over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen (Motrin IB) or aspirin, prescription drugs such as triptans or ergotamines, or hormone therapy for women.
If you experience frequent migraines, your doctor may also suggest preventive treatments, such as daily exercise, drinking lots of fluids, getting enough sleep, losing weight if necessary, or avoidance of certain foods or drinks that trigger headaches. Some people find relief from using a cold pack on their forehead or neck or by massaging their temples.
chronic headache:
A chronic headache is a type of headache that lasts for days, weeks, or even months. Chronic headaches can be complicated to treat and often require the help of a specialist.
There are several types of chronic headaches, including:
-Tension headaches
-Migraines
-Cluster headaches
-Sinus headaches
Rebound headache:
The overuse of pain medications causes rebound headaches. If you take pain medication more than two days a week, you’re at risk of developing rebound headaches. Rebound headaches are usually worse than the original headache and can last for hours or days.
To avoid rebound headaches, try to:
-Take medication only when you experience a headache
-Use the lowest effective dose of medication
-Alternate between different types of pain medication
-Avoid taking pain medication for more than two days a week
-Use over-the-counter medications cautiously, if at all, as they can also cause rebound headaches.
Some people find relief from using alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage.
There are many possible causes of headaches. While the majority of headaches are not severe, it is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms along with your headache: severe pain that does not go away, blurred vision, numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, difficulty speaking, loss of balance or coordination, or loss of consciousness.
Several treatments are available for headaches, including over-the-counter and prescription medications, alternative therapies, and lifestyle changes. If you experience frequent or severe headaches, it is essential to seek medical attention to find the cause and get appropriate treatment.
Headache treatment:
There are many possible treatments for headaches, including over-the-counter and prescription medications, alternative therapies, and lifestyle changes. If you experience frequent or severe headaches, it is vital to seek medical attention to find the cause and get appropriate treatment.
The most common treatments for headaches include over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen (Motrin IB) or aspirin, prescription drugs such as triptans or ergotamines, or hormone therapy for women.
If you experience frequent migraines, your doctor may also suggest preventive treatments, such as daily exercise, drinking lots of fluids, getting enough sleep, losing weight if necessary, or avoidance of certain foods or drinks that trigger headaches. Some people find relief from using a cold pack on their forehead or neck or by massaging their temples.
Alternative therapies:
Some people find relief from using alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage. There are many possible causes of headaches. While the majority of headaches are not severe, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms along with your headache: severe pain that does not go away, blurred vision, numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, difficulty speaking, loss of balance or coordination (ataxia), and loss of consciousness (syncope).
Several treatments are available for headaches, including over-the-counter and prescription medications, alternative therapies, and lifestyle changes. If you experience frequent or severe headaches, it is crucial to seek medical attention to find the cause and get appropriate treatment.
The most common treatments for headaches include over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen (Motrin IB) or aspirin, prescription drugs such as triptans or ergotamines, or hormone therapy for women.
If you experience frequent migraines, your doctor may also suggest preventive treatments, such as daily exercise, drinking lots of fluids, getting enough sleep, losing weight if necessary, or avoidance of certain foods or drinks that trigger headaches. Some people find relief from using a cold pack on their forehead or neck or by massaging their temples.