Acute Sinusitis
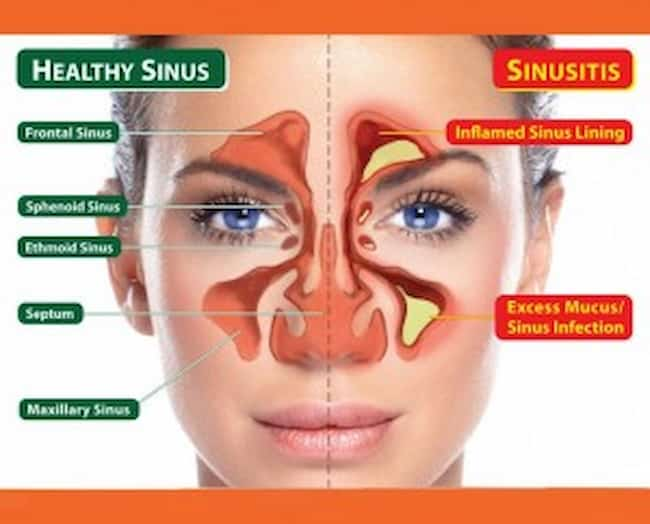
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the lining tissues of one or more sinuses. Most cases are caused by viral infections (38-72%). Bacterial causes make up 30-50%, and fungal causes account for only 2% of sinusitis cases. The symptoms include congestion, facial pain, headache, fever, poor sense of smell, and nasal discharge.
The medical treatment is with antibiotics if bacteria cause the infection. Physicians also employ analgesics to reduce facial pain, and I Nasal decongestant spray may be used to unblock swollen nasal passages to drain mucus out of the nose.
Acute Rhinosinusitis:
This condition occurs when fungi or other microbes cause infection in the mucous membranes of the nose and sinuses. The immune system responds by causing inflammation. In some cases, this leads to a build-up of fluid in the sinuses, which results in symptoms such as facial pain and pressure, headaches, fever, nasal congestion with thick green or yellow discharge, redness of eyes, or postnasal drip (mucus draining down the back of your throat).
Symptoms may develop slowly over several days, while others experience them quickly.
The medical treatment is similar to that used for acute sinusitis (antibiotics if bacteria are present; analgesics for pain etc.). However, Sinus Surgery/Endoscopic surgery might be required for drainage of accumulated fluid if that becomes a problem.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis:
This condition occurs when the inflammation of the sinuses lasts for three months or more and causes symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain and pressure, runny nose, postnasal drip (mucus draining down the back of your throat), stuffy nose, and poor sense of smell.
The medical treatment is similar to that used for acute sinusitis (antibiotics if bacteria are present; analgesics for pain etc.). However, Sinus Surgery/Endoscopic surgery might be required for drainage of accumulated fluid if that becomes a problem.
Additionally, Immunotherapy might be used to reduce inflammation caused by allergens in people whose allergies cause chronic sinusitis.
Treatment:
In acute sinusitis, rest, nasal saline irrigation, and painkillers control symptoms. Antibiotics follow this in cases where the cause is bacterial. In chronic sinusitis, warm compresses or humidifiers may help with congestion.
Nasal corticosteroid sprays or allergy medicines may be used if allergies are present. Surgery might be required for major or persistent problems with chronic sinusitis after medical treatment has failed. Additional surgery might also be needed to treat these conditions if complications occur.
chronic sinusitis:
persistent inflammation of the sinuses lasting more than eight weeks or experienced more than three times.
The most common form of sinusitis is acute, which resolves independently. Chronic sinusitis can last for years and may be caused by allergies, nasal polyps, or a deviated septum. It also predisposes to more severe conditions such as fungal infections. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), over 19 million cases of chronic sinusitis go untreated in the United States per year.
Symptoms of sinusitis include persistent facial pain, headaches, nasal congestion, and a reduced sense of smell. The most common type of sinusitis is acute sinusitis which lasts for less than eight weeks. Chronic sinusitis lasts longer than this or has been experienced more than three times.
When people experience chronic sinusitis, there are often other problems with the nose, including inflammation and swelling of the lining, polyps (small growths), mucous production, or loss of sense of smell that accompanies it. Many people will not seek treatment for chronic forms of sinusitis because it is not life-threatening but can result in serious health complications due to its effect on the immune system if allowed to continue untreated.
Chronic sinusitis treatment:
There are many different causes of chronic sinusitis, which makes some forms more challenging to treat than others. If an allergy is a cause, some form of allergen removal or modification may be helpful. Nasal polyps are often treated with medication that helps shrink them. Persistent blockage in the nasal passages can be resolved through surgery if other treatments are unsuccessful.
The mucous build-up in the sinuses is one of the most common causes of chronic sinusitis and usually responds well to treatment with saline sprays/irrigations that reduce swelling and mucous production within the nasal passages. Some people find relief by using essential oils mixed with water as a nasal spray, but this must be done cautiously so as not to cause further irritation or damage.
Using a neti pot with nasal saline is an effective way to irrigate the sinuses and remove mucous build-up and other foreign matter accumulated within them. This treatment takes some time, but it can prevent further complications such as fungal infections, which often accompany chronic forms of sinusitis without getting the proper treatment.
Acute sinusitis causes:
Acute sinusitis, also known as a cold or the flu, is a common condition caused by an inflammation of the sinuses. This inflammation makes it difficult for mucus to drain from the sinuses, causing pressure and pain in the face and head. Symptoms of acute sinusitis include fever, headache, upper respiratory infection, along with nasal congestion.
The most common form of acute sinusitis is a viral infection which typically starts as a cold or flu before developing into full-blown sinusitis.
In some cases, bacterial infections will develop when antibiotics suppress viruses, creating an opportunistic environment for bacteria to thrive within the nose and throat.
These infections are usually seen in people with compromised immune systems, such as those with cystic fibrosis, the elderly, and the very young. These forms of sinusitis require medical treatment to resolve and can result in severe complications if not addressed promptly.
Acute sinusitis headache:
The causes of sinusitis may be different, and the symptoms differ. Sinus headache is one such symptom that can be caused due to infection or other factors.
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection, allergies, chemical irritants, smoke, etc. When mucous builds up in these cavities, it becomes difficult for them to drain, leading to pain and pressure in the face, referred to as sinus headache. Other sinus headaches include cold symptoms like coughs and a stuffy nose.
Acute headaches are among the most common headaches seen in clinical practice. It has been reported that 3 out of 4 adults experience a headache in a given year, and about half of these headaches are migraines. Among other causes, sinusitis is the leading cause for triggering a tension-type or migraine-type headache.
Acute sinusitis duration:
Acute sinusitis typically lasts for approximately 4-10 days if the cause is viral. Bacterial forms of sinusitis can last much longer, sometimes several months or longer, if not adequately treated with antibiotics.
Acute sinusitis fever:
Another symptom of a sinus headache is fever experienced due to an infection such as a cold or the flu. A fever makes you feel hot and may cause sweating and lead to chills.
An elevated body temperature alone does not indicate a diagnosis of sinusitis. Still, it is one of the most common accompanying symptoms seen along with headaches and other nasal problems, including a stuffy nose and runny nose. If left untreated, chronic sinus infections can result in serious complications such as a brain abscess. Hence, it is essential to seek the proper treatment if the symptoms continue for a more extended time.
Acute sinusitis medication:
Treatment for acute sinusitis generally involves symptomatic care and antibiotics, which are only prescribed in severe cases where something more than just a viral infection is present.
Treatment with analgesics, antipyretics, antihistamines, nasal saline irrigations can relieve symptoms but not resolve the underlying problem. In rare cases, surgical interventions may be necessary when all other treatments prove unsuccessful over an extended time.
To determine the best form of therapy for you or your child’s sinusitis, it is essential to consult with a doctor who can first assess your symptoms and then determine the best course of action.